Docker Scan With Clair
Docker provides an excellent way to package application with all its dependencies. Docker images contains the application, its dependencies such as Maven or NPM packages, base Operating System and other supporting packages such as Java and NodeJS. Build pipeline is setup to create a docker image for code changes. Since the image contains all the dependencies they can be deployed to any platform that supports Docker such as on-prem Kubernetes or cloud based platforms such as AWS ECS.
Docker Image Scanning
Since the docker image contains all OS files required by the application to run there is a need to vet all packages installed in the docker image to ensure they have no vulnerabilities. Docker philosophy is to create light weight minimal containers that fulfil just one purpose. For example, different images should be created for different applications. This fits well in microservice ecosystem where a docker image is created for each microservice.
Image Scanning in Registries
Both Dockerhub and Quay provide images scanning out-of-box. However there are limitations. As of now DockerHub scan is available for private repos only by default. Image secuirty scanning is available for Quay Enterprise only.
Clair - Open Source Image Scanner
Clair from CoreOS is an open source vulnerability scanner for docker images. It aggregates vulnerabilites from vulnerability databases for different OSes such as Debian, Ubuntu, Red Hat, Alpine and Oracle Linux. Clair can be pulled as docker image to run one off scans in the bild pipeline. When you run Clair for the first time, it downloads vulnerability information from the sources to a blank database. This download can take some 20-30 minutes and is not acceptable in a CICD pipeline.
This is solved by arminc/clair-db which runs a daily build of the vulnerability database and creates pre-populated database images ready to use from the get go. This database can be run as follows:
docker run -d --name db arminc/clair-db
Clair requires a config.yaml file with configurations such as DB passwrod to start. Another image from arminc solves this by providing a default config embedded in Clair. This can be run to connect with our db as follows:
docker run -p 6060:6060 --link db:postgres -d --name clair arminc/clair-local-scan
Clair exposes an API to scan individual docker layers. To run a scan a Clair client is required that can do the job. Klar is a popular CLI client written in Go that can run point and shoot scans. However it needs the image to be scanned to be in the registry already and cannot scan images that are local. Running scans in a CICD pipeline we would prefer to run scan locally before pushing the image to the registry. Having results available before release allows us to decide wheter we should push the image or break the build based on the number and severity of vulnerabilibies in the image. Clair-scanner is another CLI client for Clair that has the ability to run local scans.
We can run clair-scanner by providing it the IP of the docker bridge gateway to run a local scan as follows:
# get docker gateway IP
DOCKER_GATEWAY=$(docker network inspect bridge --format "{{range .IPAM.Config}}{{.Gateway}}{{end}}")
# download scanner cli
wget -qO clair-scanner https://github.com/arminc/clair-scanner/releases/download/v8/clair-scanner_linux_amd64 && chmod +x clair-scanner
# run scan on local image - dubu in this case
./clair-scanner --ip="$DOCKER_GATEWAY" dubu:latest
Summing it all up
We can run a scan on a local image with the following script:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
docker run -d --name db arminc/clair-db
sleep 15 # wait for db to come up
docker run -p 6060:6060 --link db:postgres -d --name clair arminc/clair-local-scan
sleep 1
DOCKER_GATEWAY=$(docker network inspect bridge --format "{{range .IPAM.Config}}{{.Gateway}}{{end}}")
wget -qO clair-scanner https://github.com/arminc/clair-scanner/releases/download/v8/clair-scanner_linux_amd64 && chmod +x clair-scanner
./clair-scanner --ip="$DOCKER_GATEWAY" dubu:latest
CI/CD Integration
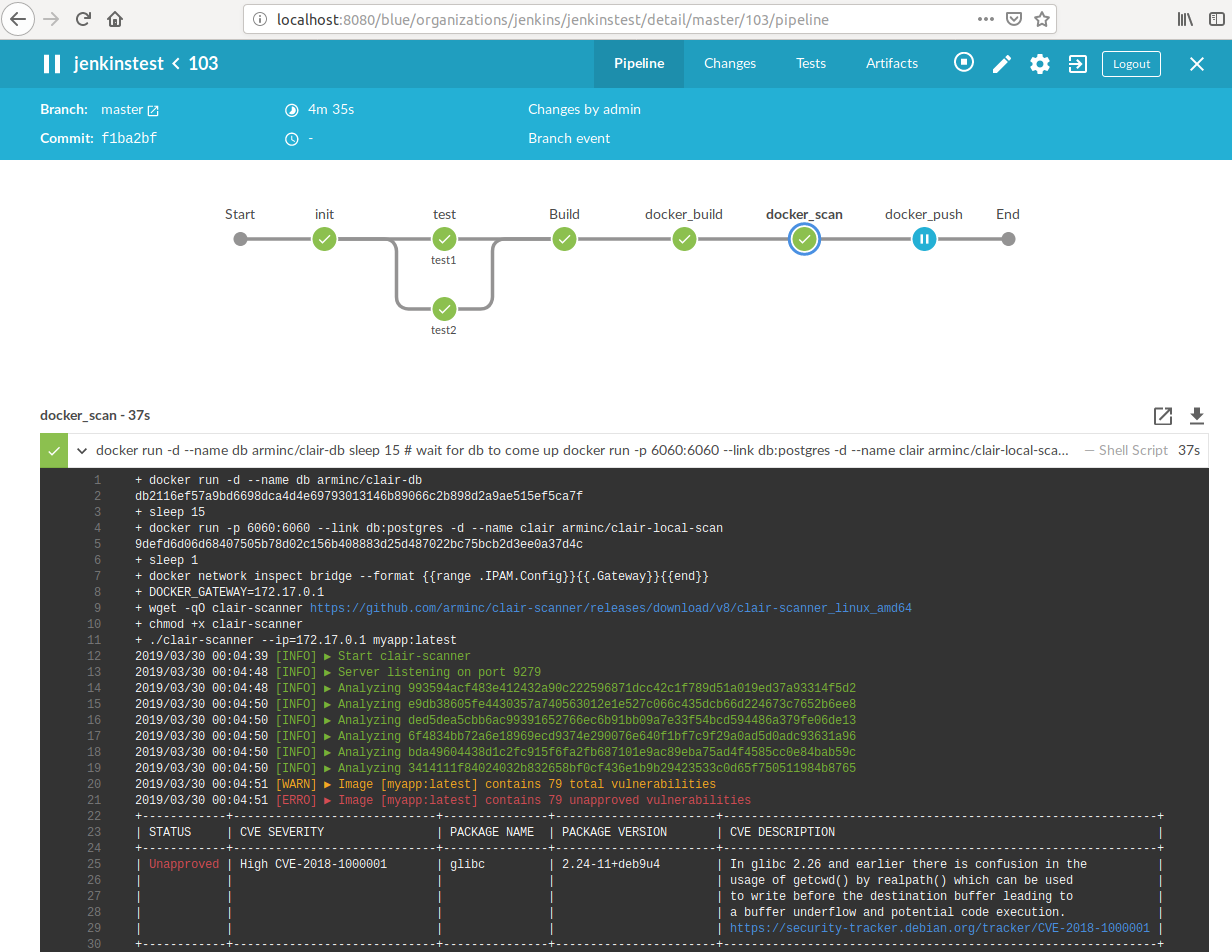
This script can be run in a Jenkins pipeline as follows:
stage("docker_scan"){
sh '''
docker run -d --name db arminc/clair-db
sleep 15 # wait for db to come up
docker run -p 6060:6060 --link db:postgres -d --name clair arminc/clair-local-scan
sleep 1
DOCKER_GATEWAY=$(docker network inspect bridge --format "{{range .IPAM.Config}}{{.Gateway}}{{end}}")
wget -qO clair-scanner https://github.com/arminc/clair-scanner/releases/download/v8/clair-scanner_linux_amd64 && chmod +x clair-scanner
./clair-scanner --ip="$DOCKER_GATEWAY" myapp:latest || exit 0
'''
}
clair-scannerby default breaks the build if any issues are found. We ignore the exit code by appending|| exit 0.
This will result in a summary and detailed table of issues:
Leave a comment